Banner Image Courtesy of 3Dnatives
Metal 3D Printing, CNC Machining, and Metal Casting Explained
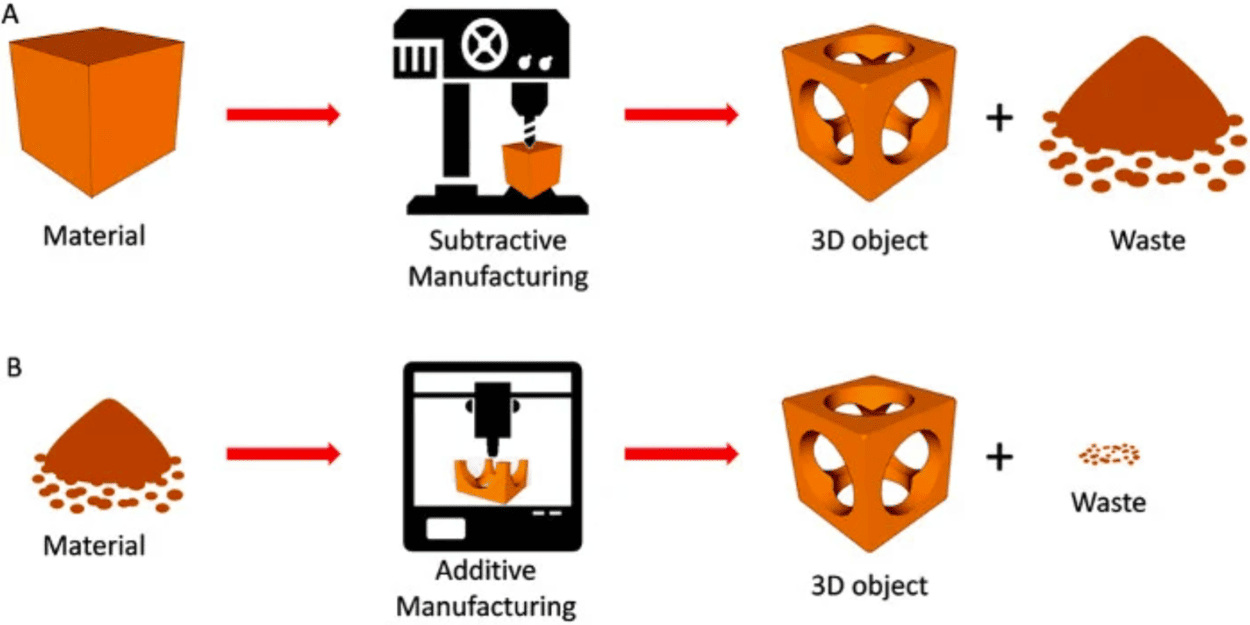
Metal 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
Metal 3D printing builds parts layer by layer using powdered metals fused by lasers, electron beams, or binding agents. Popular technologies include:
• Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): lasers melt metal powder into solid layers.
• Binder Jetting: a liquid binder glues powder particles, later sintered in a furnace.
• Electron Beam Melting (EBM): uses an electron beam instead of a laser.
Metal 3D printing enables complex geometries, lightweight structures, and rapid prototyping. Materials range from stainless steel and titanium to aluminum and super alloys.
CNC Machining (Subtractive Manufacturing)
CNC machining removes material from a solid block (metal billet) using computer‑controlled cutting tools. Common processes include:
• Milling: rotating cutters remove material to create shapes.
• Turning: lathes spin the workpiece while cutting tools shape it.
• Drilling: precise holes are created.
CNC machining is prized for precision, repeatability, and versatility. It works with almost any machinable metal, from aluminum and brass to hardened steels.
Metal Casting
Casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold, letting it cool and solidify. Variants include:
• Sand Casting: inexpensive, flexible, ideal for large parts.
• Investment Casting: wax patterns create detailed molds for complex shapes.
• Die Casting: molten metal injected into steel molds for high‑volume production.
Casting is one of the oldest manufacturing methods, valued for scalability and cost efficiency in mass production.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Metal 3D Printing
Pros
• Enables intricate geometries impossible with traditional methods
• Rapid prototyping and customization
• Lightweight designs with internal lattices
• Minimal material waste
Cons
• High per‑part cost compared to machining or casting
• Limited scalability for mass production
• Requires post‑processing (heat treatment, machining, polishing)
• Smaller build volumes than casting or machining
CNC Machining
Pros
• Extremely high precision and tight tolerances
• Wide material compatibility
• Mature, reliable technology with global availability
• Excellent surface finish with proper tooling
Cons
• Material waste due to the subtractive process
• Less efficient for highly complex geometries
• Set up time and tooling costs for new designs
• Not ideal for very high‑volume production compared to casting
Metal Casting
Pros
• Cost‑effective for large production runs
• Strong mechanical properties from solidification
• Suitable for very large parts
• Wide range of alloys available
Cons
• Long lead times for mold design and setup
• Limited design flexibility compared to 3D printing
• Surface finish often requires machining or polishing
• Dimensional accuracy is lower than CNC machining
Comparison by Key Factors
|
Factor |
Metal 3D Printing |
CNC Machining |
Metal Casting |
|
Production Speed |
Fast for prototypes, slower for mass production |
Moderate, depends on complexity |
Slow setup, fast for high volumes |
|
Design Flexibility |
Excellent, supports complex geometries |
Good, but limited by tool access |
Moderate, mold constraints apply |
|
Material Options |
Growing range, but limited vs machining |
Very broad, almost all machinable metals |
Wide range of alloys |
|
Accuracy & Tolerances |
High, but requires post‑processing |
Very high precision |
Moderate, depends on casting type |
|
Surface Finish |
Requires polishing/machining |
Excellent with proper tooling |
Often rough, needs finishing |
|
Cost Structure |
High per part, low tooling |
Moderate setup, efficient for small batches |
High tooling, low per‑part cost |
|
Scalability |
Limited |
Moderate |
Excellent for mass production |
|
Sustainability |
Less waste, but energy‑intensive |
Wasteful, but recyclable chips |
Energy‑intensive, mold waste |
Best Applications
Metal 3D Printing
• Aerospace: lightweight brackets, turbine components
• Medical: patient‑specific implants, surgical tools
• Automotive: prototypes, performance parts
• Research: experimental designs, rapid iteration
CNC Machining
• Automotive: precision engine components, transmission parts
• Industrial: tooling, fixtures, custom equipment
• Defense: high‑tolerance parts for weapons systems
• Consumer products: electronics housings, luxury goods
Metal Casting
• Automotive: engine blocks, cylinder heads
• Industrial: pumps, valves, heavy machinery parts
• Jewelry: intricate designs via investment casting
• Large‑scale production: cookware, hardware, construction components
Choose the Right One for Your Projects
Choose Metal 3D Printing if:
• You need prototypes or low‑volume production
• Your design involves complex geometries or lightweight structures
• Customization is critical (e.g., medical implants)
Choose CNC Machining if:
• You require high precision and tight tolerances
• You’re producing small to medium batches
• Material versatility is important
Choose Metal Casting if:
• You’re producing large volumes of parts
• Cost efficiency is a priority
• Part size is large or requires strong mechanical properties